Battery types – Lead acid, AGM, EFB
This article contains:
Starter batteries have proved themselves in millions of cars throughout the world. With continuous innovations and further developments, over the years classic wet batteries have increased in performance, reliability and versatility. EFB and AGM batteries are new battery types, which cater for the increased demands of the present generation of vehicles.
AGM, EFB, Lead Acid: Three different battery types – many common features
AGM and EFB batteries are characterized by their high performance. In spite of their different technological approaches, the latest generation of battery types have further positive features in common: They need less maintenance and are more reliable than 10 years ago – thanks to advances in battery technology.
Just a few decades ago, the acid level in a car battery had to be regularly checked and topped up with distilled water if necessary. With modern, maintenance-free batteries, water loss is so low that topping up with distilled water is not necessary during the life of the battery.
Starter batteries, EFB batteries and AGM batteries: The differences between battery types
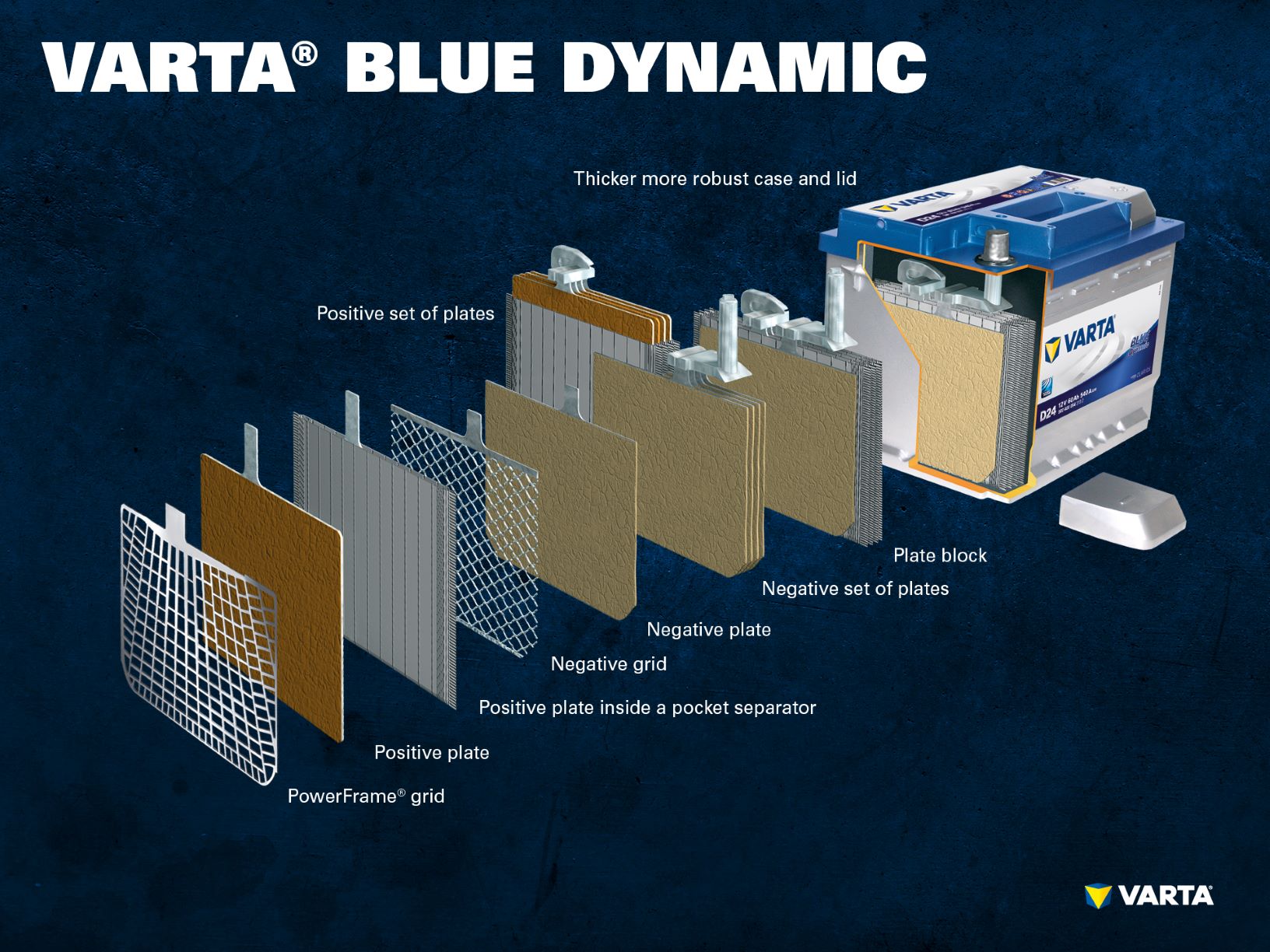
- Wet cell batteries (SLI) – proven and economical
A conventional starter battery consists of six battery cells. A battery cell, also referred to as a plate block, consists of a positive and a negative set of plates, which in turn consists of several electrodes.
A positive electrode consists of active material made from lead oxide and a positive grid made of lead alloy. The grid structure gives the electrodes a solid structure and at the same time serves as an electrical conductor. The active material is immersed in an electrolyte, a mixture of acid and distilled water.
A negative electrode also consists of active material, however in this case made of pure lead, and a negative grid. The electrodes with different polarities are separated by a separator. The required battery capacity is achieved by connecting the individual plates in the cell in parallel. Connecting the individual cells in series produces the required voltage of 12 Volt.
Do you want to know more? You can find out how a battery functions in our article about the structure and function of starter batteries.
Conventional batteries such as lead-acid batteries are the most common types of battery. This technology is often referred to as SLI, which relates to the main functions of a vehicle battery: Starting, Lighting, and Ignition. They are suitable for vehicles without start-stop technology and a moderate number of electrical consumers.
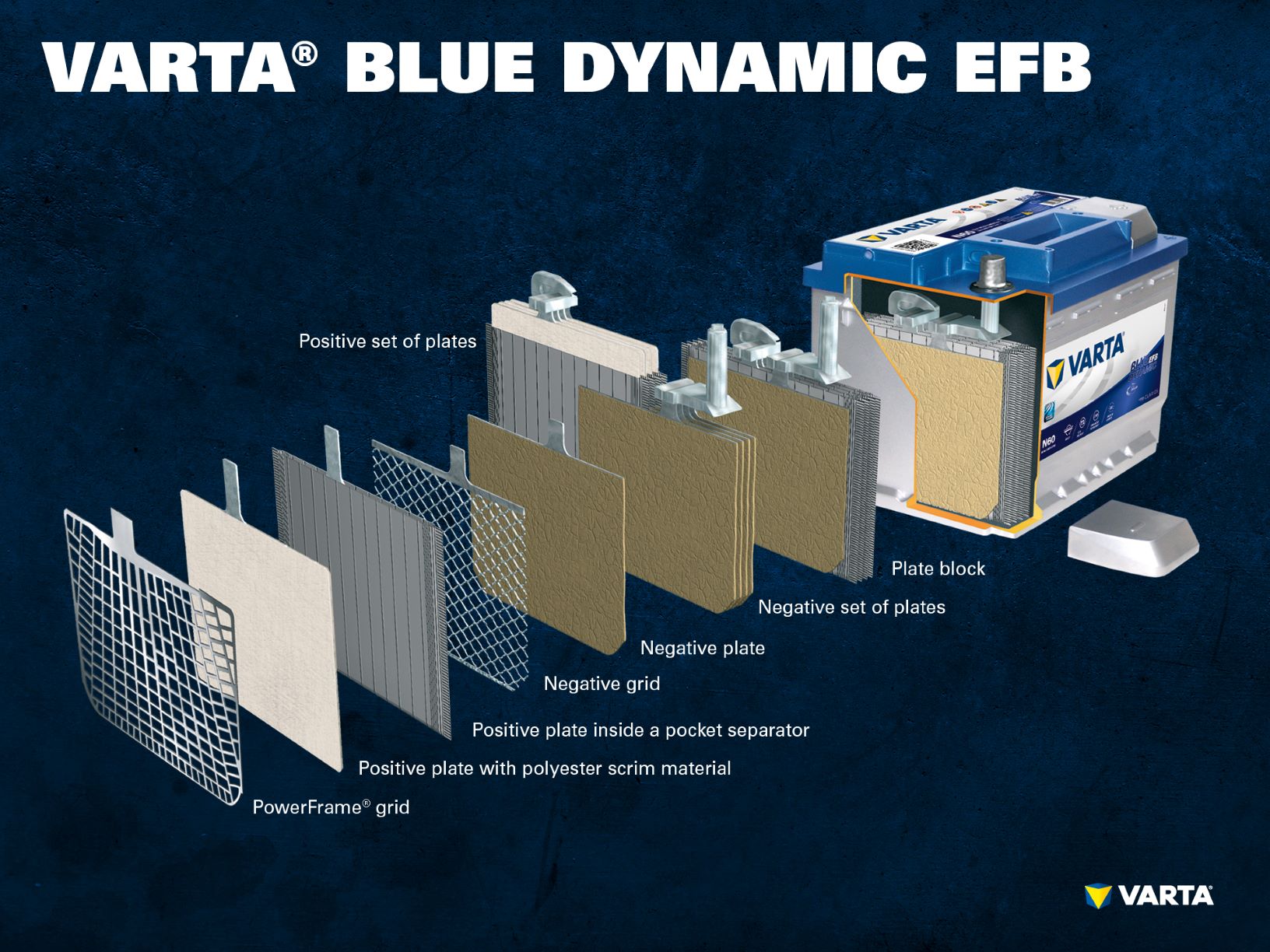
- EFB batteries – many charging cycles and long life
EFB batteries are an optimized, higher performance version of the wet battery. The abbreviation “EFB” stands for “Enhanced Flooded Battery”. Here too, the plates are insulated from each other with a microporous separator. Between the plate and the separator there is also a polyester scrim. This material helps to stabilize the active material of the plates and extend the life of the battery. EFB batteries have a large number of possible charging cycles and provide more than double the partial and deep discharge performance in comparison with conventional batteries.
EFB batteries are often installed in vehicles with simple automatic start-stop systems. Due to their superior performance batteries with EFB technology are also increasingly used as replacements for conventional lead-acid batteries.
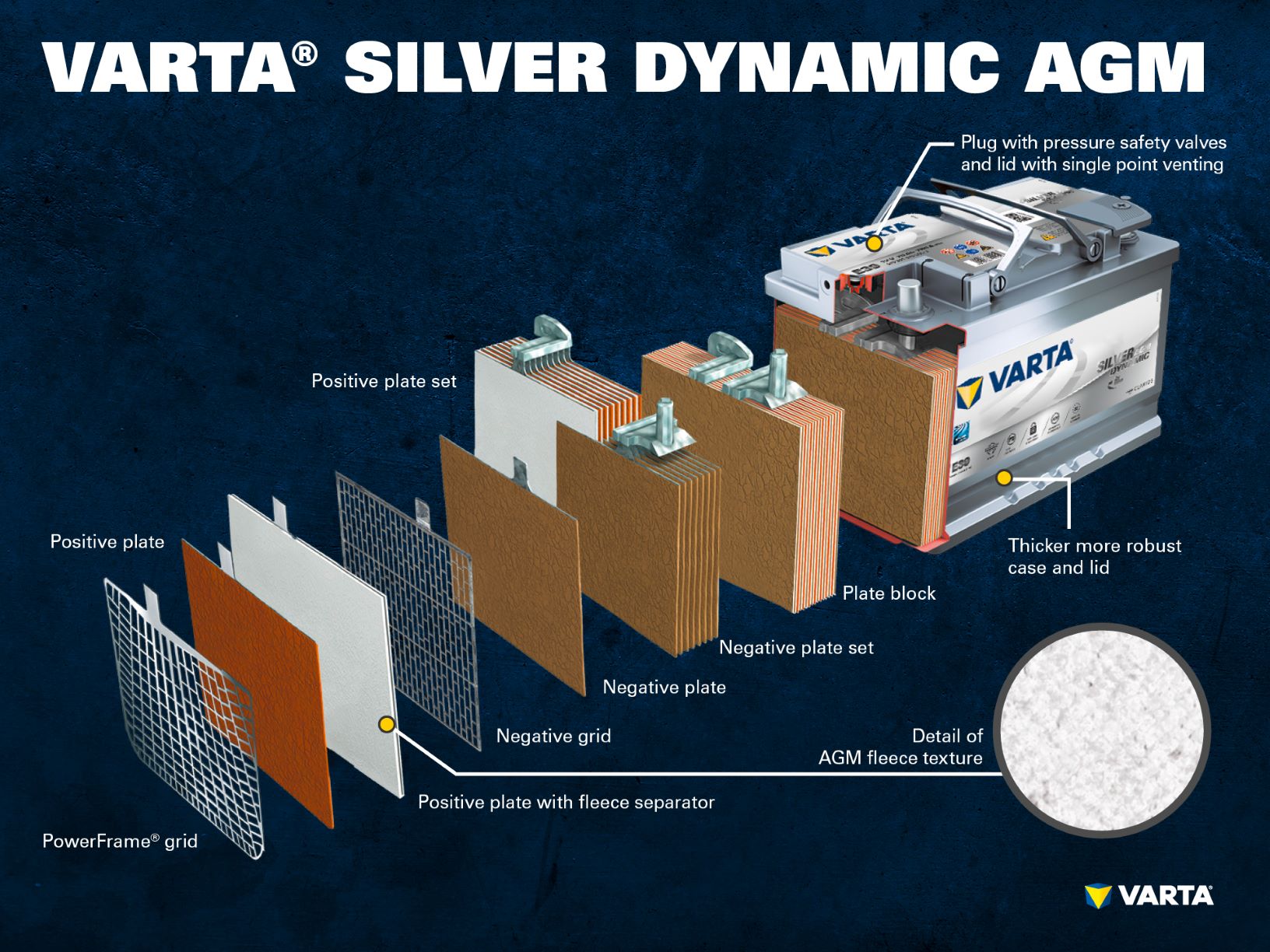
- AGM batteries – high performance and load capacity
AGM batteries are versatile, have high performance and are designed for high demands. In principle, the structure of an AGM battery is the same as that of a wet cell battery. However, in an AGM the electrolyte is no longer free-floating, but rather is bound in a special glass fiber separator – hence the name “Absorbent Glass Mat”. The large contact area contributes to the power output and also makes the battery leak-proof. Due to its construction, the battery is sealed airtight. This feature enables internal recombination of oxygen and hydrogen, so that there is no water loss. To protect against excess pressure, the individual battery cells are equipped with a safety valve, so that they remain safe, even in case of a fault.
With regard to their service life, AGM batteries have significant advantages over simple starter batteries. An AGM battery can withstand three times more cycle life than a conventional starter battery. A further advantage of AGM batteries is that they are not dependent on their position, as due to the binding of the electrolyte, no liquid can escape. Even if the battery case is fractured, no battery acid can escape.
AGM batteries are ideal for vehicles with automatic start-stop systems with braking energy recovery (recuperation), as a conventional starter battery cannot handle the high power demands of these systems. AGM batteries are also the right choice for cars with high energy consumption and a large number of electrical consumers.
Which battery for which vehicle?
In the VARTA Partner portal, our partner workshops can quickly find the right replacement battery, its position in the vehicle, as well as installation and removal instructions for most vehicles which are in use in Europe. The VARTA battery search is also a helpful tool for our end customers to decide which is the right replacement battery for their vehicle.
Under certain circumstances, an upgrade to a different battery technology may be worthwhile. Here, you can read about when this is the case. An AGM battery must always be replaced with an AGM battery. If a conventional battery is installed in a start-stop vehicle, a significant reduction of battery life or restrictions in the function of the vehicle’s Energy Management System must be expected. This also applies if the start-stop function is deactivated.

