Why won’t the car start – is it because of the battery?
This article contains:
Make sure that your car will always start: How to prevent battery discharge
All drivers dread this noise: When they turn the ignition key or press the starter button, there is only a tired groaning sound. After a few more attempts to start, the starter finally gives up. The car won’t start. The reason for starting difficulties is usually that the battery is poorly charged. Automatic start-stop systems, air conditioning, seat heaters, modern entertainment systems and other electrical consumers all put a strain on the battery. It is therefore essential that a powerful battery is used to cater for the increased demands in modern vehicles.
Our quick check: The most common reasons for a dead battery
- “Energy guzzlers”
Heating elements in the steering wheel and the driver and passenger seats, as well as the windshield and rear window heaters are real “energy guzzlers” and put a heavy load on the battery. Especially in modern vehicles with a start-stop function, the battery plays a key role in the vehicle system. It ensures that when the engine is switched off, for example at traffic lights, not only the radio and the air conditioning system continue to function. In some cases it also simultaneously supplies the necessary power to up to 150 different electrical consumers. And it still has enough power to start the engine again when the traffic lights turn green. Modern car batteries are genuine power packs, but they also need to be checked at regular intervals. Although modern batteries are maintenance-free, they need regular checks of the state of their charge (SOC) and state of health (SOH) in order to detect imminent battery failures before they can cause a complete breakdown.
- Silent consumers
Silent consumers are the electrical components in the car which cause battery discharge even when the vehicle is switched off. Consumers such as alarm systems, clocks or keyless entry systems remain in standby mode, even when the vehicle is switched off, and therefore cause a continuous discharge of the battery. Even though the power consumption is only small, it has a negative effect on the state of charge of the battery due to its continuous action. After longer standstill periods, for example in the case of long holidays, it is possible that the car may not start due to a discharged battery.
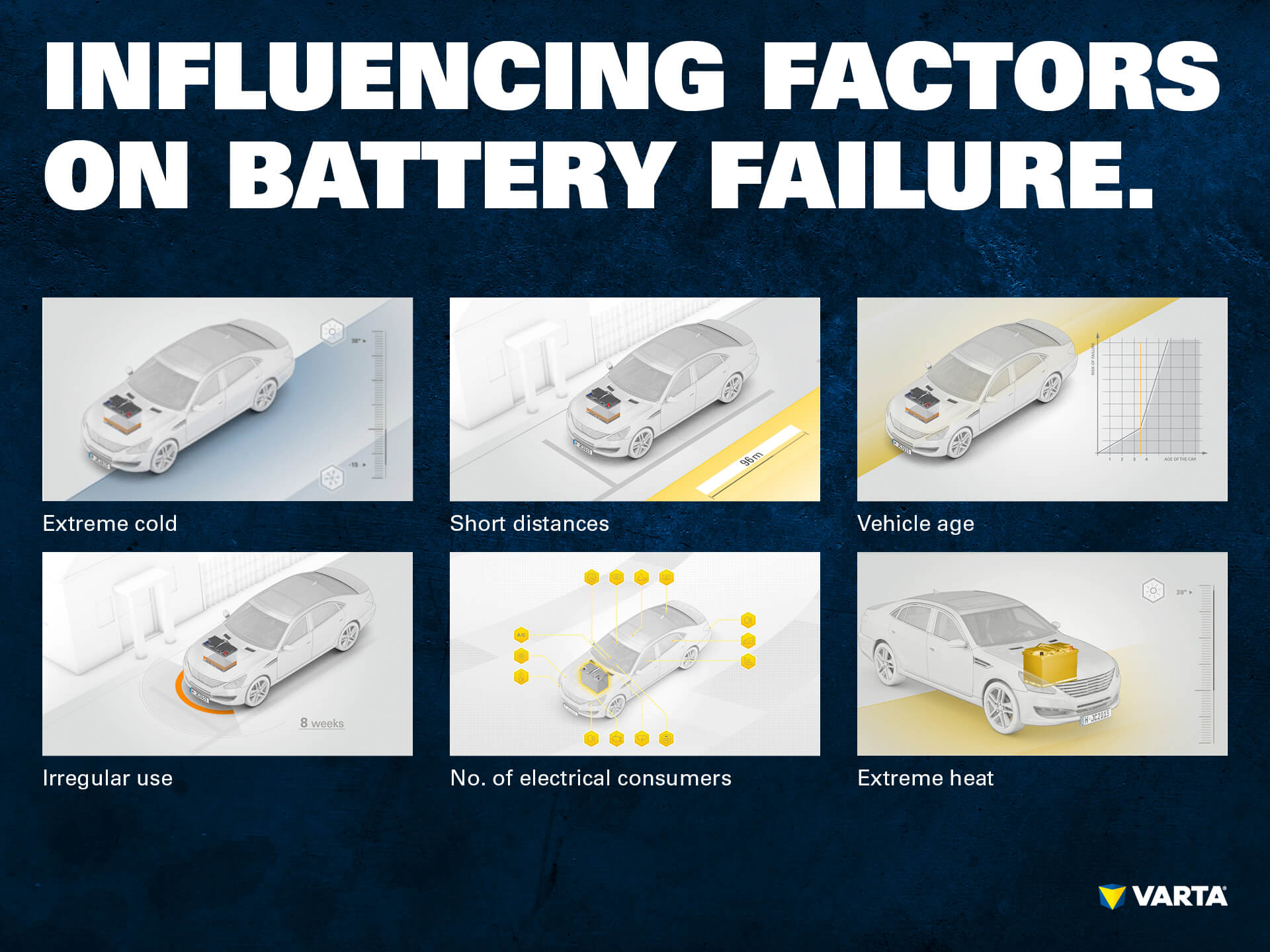
- Extreme temperatures
The weather also has an effect on the state of charge of car batteries. Both heat and cold put a strain on the battery. Especially at sub-zero temperatures, starting problems are more common. The reason: At low temperatures, the electro-chemical reactions in the battery take place more slowly. The electrons only travel slowly, which reduces the starting power of the battery. At low temperatures, starting is also made more difficult by the thickness of the engine oil, because at temperatures below 0° C it becomes highly viscous. The starter motor needs a higher starting current to overcome this resistance. As well as this, there is an increased load due to demanding consumers such as heaters and ventilators. Low temperatures not only affect the starting power. Recharging of the battery is slower due to the cold, so that the battery needs more time to become fully charged. In addition, the maximum power output of the alternator is limited. If a large number of consumers are active, little energy remains to charge the battery.
Hot days may also cause starting problems. Outside temperature above 20° C accelerate the chemical processes in car batteries which promote self-discharge or corrosion.
Regardless of winter or summer temperatures: A large number of start-stops or stop-and-go travel, for example on the motorway, also contribute to a heavier load on the battery.
By the way…
Although battery life can be extended with proper care, just like tires and brakes, batteries are wearing parts, which only have a limited life. Because of this, the battery should be tested at every visit to the workshop. Many workshops offer a battery test with the aid of suitable battery testers.
Interesting facts about power, state of charge and battery life
After a large number of charging cycles and toward the end of their useful life, conventional starter batteries (SIL) only have a capacity of 20%. With the same load, EFB batteries still have 50%. The more powerful AGM batteries can withstand four times as many charging cycles as SLI batteries and still provide 80% of their energy. Deep discharge of the battery should always be avoided, as this causes permanent damage to the battery cells. Although deep discharged batteries can be “revived” with a suitable charger, the damage which has been sustained still remains.
In case of deep discharge, immediate recharging is essential. The longer the battery remains in the deep discharged state, the more serious the damage to the battery.

